Route Calculations
Calculating a vessel’s ETA is crucial for managing the logistics of incoming and outgoing shipments, passengers, and goods. Knowing the precise ETA enables the port manager to make informed decisions about scheduling, resource allocation, and operational planning. Additionally, it plays a critical role in security, as it allows authorities to prepare for inspections, monitor vessel movements, and respond proactively to potential threats or irregularities.
The MDA API allows users to retrieve a vessel’s ETA by making a request to a specific endpoint.
This article will cover the different endpoints and their functionality.
- Calculate Vessel:
- Get predicted route to a port
The base url for the endpoints specified in this article is as follows:
http://demo.ghmaritime.com/api/portserver/Calculate Vessel ETA to a Port
To get the ETA of a vessel to a port, construct a POST request to the endpoint /ship/route, where the request body contains the source and destination, which corresponds to the vessel (source) and port (destination).
The API will start a job, meaning it will start calculating the ETA for the specified vessel, and send a JSON-encoding of the job id, as its’ response.
Once the job is completed, it is possible to construct a GET request to the same endpoint, except the id of the job is concatenated at the end of the endpoint /ship/route/{job_id}, which will return a JSON object, that contains the ETA, represented as a date, for that specific vessel.
Visualization of the process is depicted below:
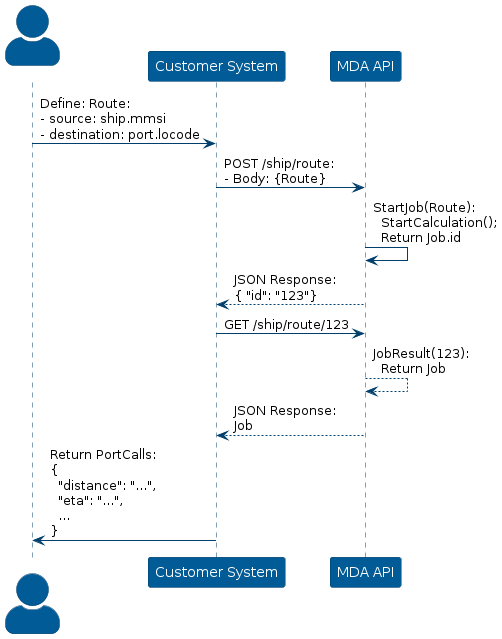
Additionally, the JSON response from the API contains the estimated route, that the vessel will follow to the port.
Calculate Vessel ETA to Point
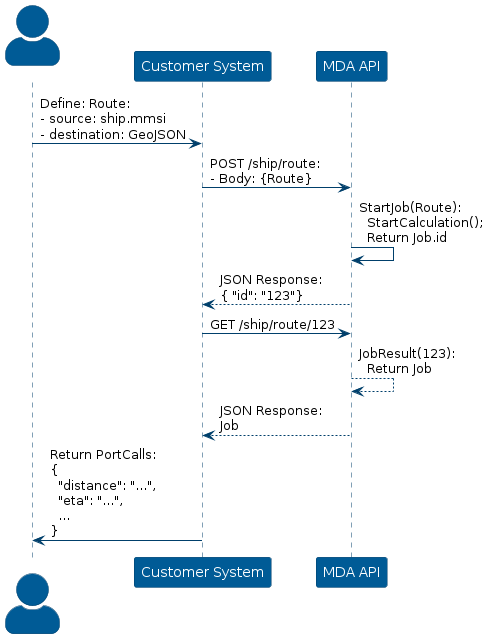
To get the ETA for a vessel to a specified point on the map, construct a POST request via the /ship/route endpoint, where the request body contains the source (ship information) and the destination (coordinates of the point).
GET /ship/routeThe destination of the route should be defined in the GeoJSON format, where it contains the latitude and longitude values of the point.
Once the API receives the request, it will create the job in the MDA system and return the id of the job.
The system will then begin to compute the ETA behind the scenes.
Once the job is completed, it is possible to construct a GET request with the id concatenated to the endpoint url, /ship/route/{id}. The API will then return a JSON object that specifies the computed ETA and several other information parameters.
Visualization of the process:
Calculate Estimated Route to a Port
To get the estimated route to a port for a vessel, follow the steps explained in Calculate Vessel ETA to a Port.
The JSON response from the API contains the estimated route represented as a list of coordinates.
